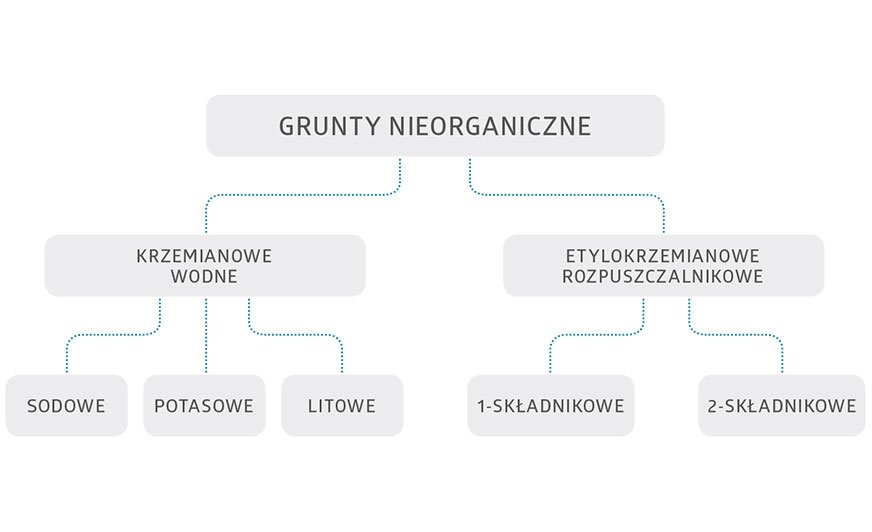
Rysunek 1. Podział gruntów nieorganicznych pigmentowanych cynkiem w zależności od rodzaju spoiwa.
Witold J. Świątkiewicz
FROSIO Inspektor Level III
LITERATURA
Munger Charles G., Zinc-Rich primers, Good Painting Practice, Steel Structures, Painting Manual Vol. 1 chapter 4.2
Steel Structures Painting Council (SSPC), Paint specification No. 20 Zinc-Ric Primers (Type I, „Inorganic,” and Type II, „Organic”)
PN–EN ISO 12944–5: 2018 Farby i Lakiery – Ochrona przed korozją konstrukcji stalowych za pomocą ochronnych systemów malarskich – część 5: Ochronne systemy malarskie.
Zubielewicz Małgorzata, Nieorganiczne i organiczne farby o dużej zawartości cynku, Farby i Lakiery 4 / 2010, 3-9
Munger C.G., Corrosion Prevention by Protective Coatings, National Association of Corrosion Engineers – USA, 1984.
Francis Rob, IOZ Coating Surface Preparation Is Easier than You Think, www.corrosionpedia.com, 2015
Francis Rob, What Do You Know about Inorganic Zinc Coatings?, Materials Performance, 6/2016
Vincent L.D. ”Lou”, Inorganic Zincs-How Do They Cure?, Coating & Linings, Phorgotten Phenomena, Materials Performance, May, 2008, 42–43
ASTM D520-00 (2011),Standard Specification for Zinc Dust Pigment
Salome Fred, Climatic conditions for successful application of zinc-rich coatings, CTI Consultants Pty Ltd, ACA 1 – Second Edition Published 2013 „Inorganic Zinc Coatings – History, Chemistry, Properties, Applications and Alternatives”,92
Szokolik A., Organic Zinc Silicates as Single-Coat Protective Systems for Steel, ACA 1 – Second Edition Published 2013 „Inorganic Zinc Coatings – History, Chemistry, Properties, Applications and Alternatives”,76